
化学反応(かがくはんのう)とは、原子間の結合の生成、あるいは切断によって異なる物質を生成する変化のことである。Any chemical reaction in which the oxidation numbers (oxidation states) of the atoms are changed is an oxidation - reduction reaction. Such reactions are also known as redox reactions, which is shorthand for reduction-oxidation reactions.
Oxidation and Reduction
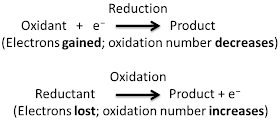
Oxidation involves an increase in oxidation number, while reduction involves a decrease in oxidation number. Usually the change in oxidation number is associated with a gain or loss of electrons, but there are some redox reactions (e.g., covalent bonding) that do not involve electron transfer. Depending on the chemical reaction, oxidation and reduction may involve any of the following for a given atom, ion, or molecule:
· Oxidation - involves the loss of electrons or hydrogen OR gain of oxygen OR increase in oxidation state
· Reduction - involves the gain of electrons or hydrogen OR loss of oxygen OR decrease in oxidation state
Reactions involving oxidation and reduction processes are very important in our everyday world. They make batteries work and cause metal to corrode (or help to prevent their corrosion). They enable us to obtain heat by burning fuels--in factories and in our bodies.
Many redox reactions are complex. However, combustion and synthesis (from elements) are two ordinary examples which require very little description. Just a little more involved is the displacement reactions. These processes are divided into three categories: hydrogen displacement, metal displacement, halogen displacement.
Example of an Oxidation Reduction Reaction
The reaction between hydrogen and fluorine is an example of an oxidation-reduction reaction:
H2 + F2 → 2 HF
The overall reaction may be written as two half-reactions:
H2 → 2 H+ + 2 e− (the oxidation reaction)
F2 + 2 e− → 2 F− (the reduction reaction)
There is no net change in charge in a redox reaction so the excess electrons in the oxidation reaction must equal the number of electrons consumed by the reduction reaction. The ions combine to form hydrogen fluoride:
H2 + F2 → 2 H+ + 2 F− → 2 HF
Importance of Redox Reactions
Oxidation-reduction reactions are vital for biochemical reactions and industrial processes. The electron transfer system in cells and oxidation of glucose in the human body are examples of redox reactions. Redox reactions are used to reduce ores to obtain metals, to produce electrochemical cells, to convert ammonia into nitric acid for fertilizers, and to coat compact discs.


No comments:
Post a Comment